How to Become a Data Scientist in 2022
An introduction to enclosures: choosing the right material - volume ii
An Introsuction to Enclosures: Choosing the Right Material - Volume II
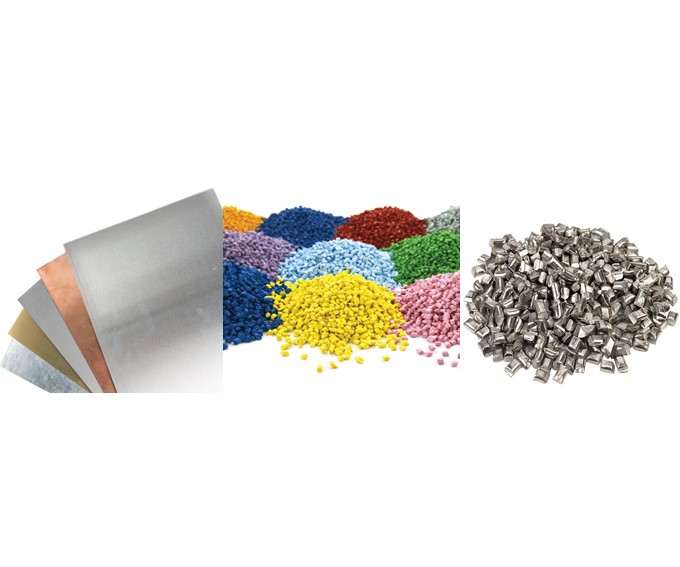
The right selection of materials for enclosure manufacturing is a complicated task which requires skill in industrial design, management and marketing. The enclosure material which houses sensitive electronic and automation components will impact their lifespan, functionality, and performance. Of the numerous materials available, each offers different protective advantages.
- Various types of plastics: ABS, ABS+PC, EK, PC, PE, PVC, PMMA, polyamide plastics, etc.
- Woods – various wood species, including composite combinations, such as wood + plastic
- Metals – production of enclosure parts from stainless steel, aluminum, aluminum-magnesium alloys, using various technologies (stamping, molding, milling, extrusion molding)
Thinking Through your Application
Before choosing a material, it’s important to think about the material qualities that your application requires.
- Aesthetic appearance of your enclosure
- Will your device feature an internal wireless antenna that needs to transmit radio frequency signals?
- Potentially subject to heavy impacts?
- Strength and weight restrictions will affect my enclosure selection
- Working environmental conditions: weather, temperature, humidity, corrosion resistance.
- Strength and weight restrictions
- Metallic or No-metallic
1. ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene)
ABS is a two-phase polymer blend that provides good all-round performance for electronic enclosures. For that reason, ABS is used in most cases in the OKW range. It is best suited for use in enclosed rooms but is less suitable for outdoor use. (Need something tougher? Specify Polycarbonate instead.
2. ASA+PC Blend (Acrylonitrile Styrene Acryl ester and Polycarbonate)
Blending ASA with PC boosts performance at high temperatures and also increases the impact strength. Combining these plastics also provides good resistance against chemicals and weather.
3. PA (Polyamide)
Polyamide is tough, wear-resistant and has good sliding properties. It also offers very good electrical insulation properties (it is used for power tool housings and cable ties)
4. Cold Rolled Steel
Cold rolled steel is ideal for general purpose indoor enclosures. However, it will rust if not coated, so bare metal and grained finishes are not recommended. It can be extremely durable indoors when finished with powder coat.
5. Stainless Steel
Stainless steel is the premium solution to corrosion resistance, because of its chromium and nickel content. However, that chromium and nickel comes at a cost and makes stainless more expensive than cold-rolled steel, aluminium or galvaneal. It is good for use with general purpose enclosures if corrosion or aesthetics are a concern.
6. Aluminium
Aluminium is one of the most lightweight metals for enclosures, however to get to the same stiffness as cold-rolled steel, it requires a thicker gauge. It does not have to be chem filmed form electrical contact, but chem film will increase the durability of aluminium
7. Galvanneal
Galvanneal is a low-carbon steel coated with zinc and annealed for the zinc to bond via diffusion into the substrate. This prevents it from flaking off when formed or bent. The finish acts like a primer and easily adheres to paint, and creates a rust-proof surface as well. Galvanneal is much more durable than cold-rolled steel in wet environments, but less so than aluminum or stainless steel. Galvanneal offers good paintability, corrosion resistance, and formability.
8. Copper
While we do offer copper within our sheet-metal offerings, it is very rarely used as the material option for an enclosure. Copper offers excellent electrical conductivity; however it is extremely soft, and thus not ideal to form an enclosure. Copper is very expensive, especially compared to other sheet-metal materials.
Application of Respective Enclosure based on material
For the majority of modern applications plastic construction is the favorable choice as it’s typically lighter, less expensive and easier to include built-in internal mounting options for quick installation. However, metal enclosures are useful for applications which require protection from potentially heavy external knocks, such as building sites, mining and quarrying. Further specific applications are discussed.
- Plastic PCB enclosures
- ABS Plastic: This material has a shiny surface that is amplifiable, resistant to concentrated acids, waterproof, and has temperature-independent impact resistance.
- Polycarbonate Plastic: This material offers fire retention and is resistant to acidic environments. It also has a high impact resistance.
- Polyester Plastic: This material offers moisture and chemical resistance. It is also lightweight and has excellent insulation properties.
- PVC Plastic: This material is durable and has high impact resistance. It is also recyclable and provides UV degradation-resistance.
- Materials used in industrial enclosures
- Painted carbon Steel: This steel has higher carbon content making it more malleable, durable and better heat distributor. The metal can resist solvents, alkaline and acids commonly used for indoor enclosures.
- Stainless Steel: Type 304 and Type 316 is the most common types of stainless steel used in enclosures. It is well suited for marine and pharmaceutical environments while type 304 is ideal for cleaning process.
- Fiberglass Reinforced Plastic: Fiberglass is used where there is high temperature and high corrosive environment, it will protect the contents even if the enclosure is fully submerged in water.
- Polycarbonate: Made from thermoplastic polymers, has a greater resistance than fiberglass, resistant to UV light deterioration and is super easy to produce holes and cutouts.
Recently Published
Popular Newsletters
Most Viewed
How to Write and Publish an Academic Research
Various domains for final year project of an
ENGINEERING PROJECT IDEAS FOR FINAL YEAR STUDENTS Engineering
SELECTING THE RIGHT PROJECT FOR FINAL YEAR Selecting
AIR QUALITY MONITORING SYSTEM BASED ON IOT USING
Trending
Contact for complete guidance
Address List
- # 28, 1st Main Road,1st Cross, Shakthi Garden, Kalyan Nagara, Bengaluru-72
- +91-968-696-3065
- eng@pincore.in